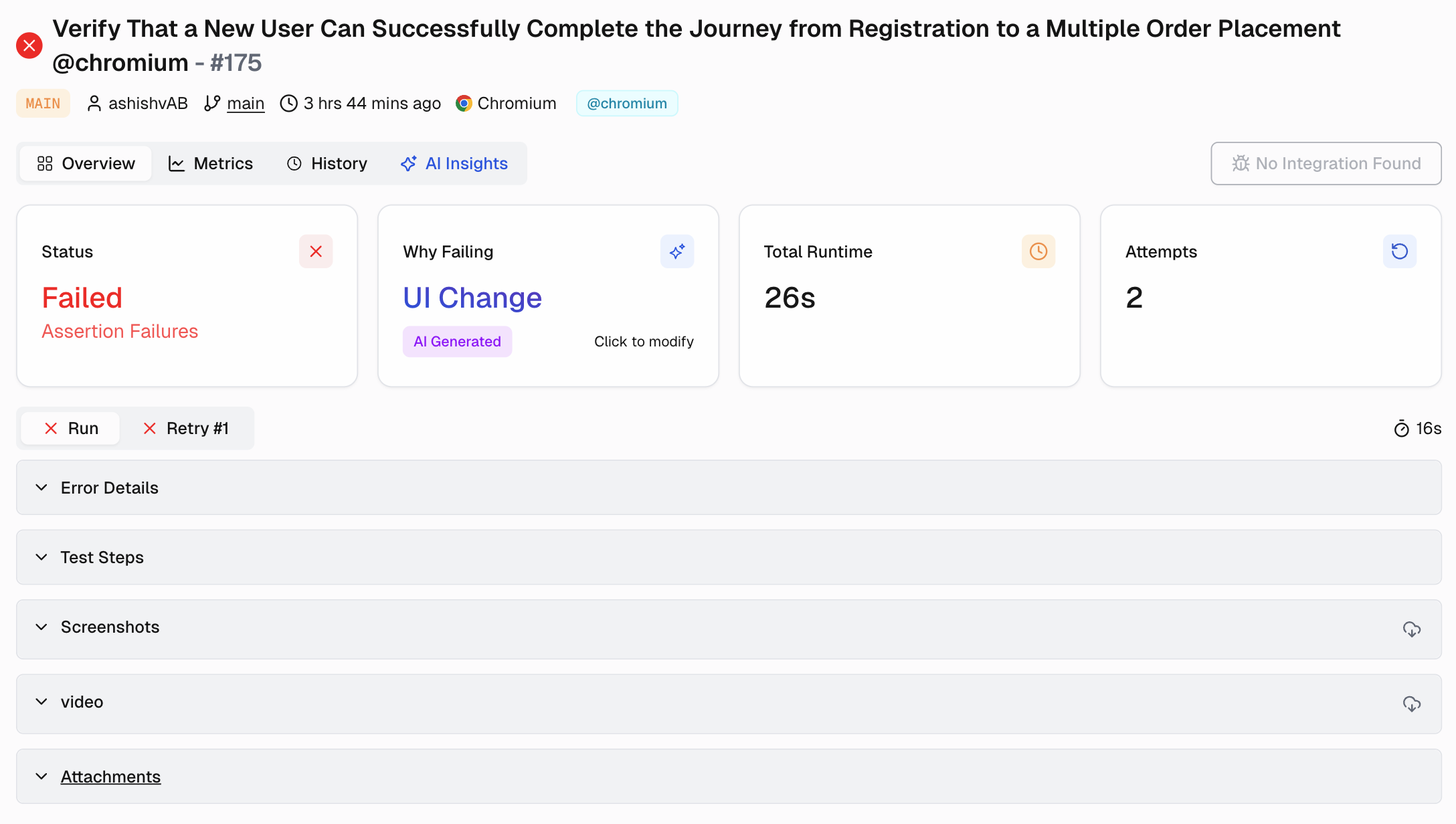
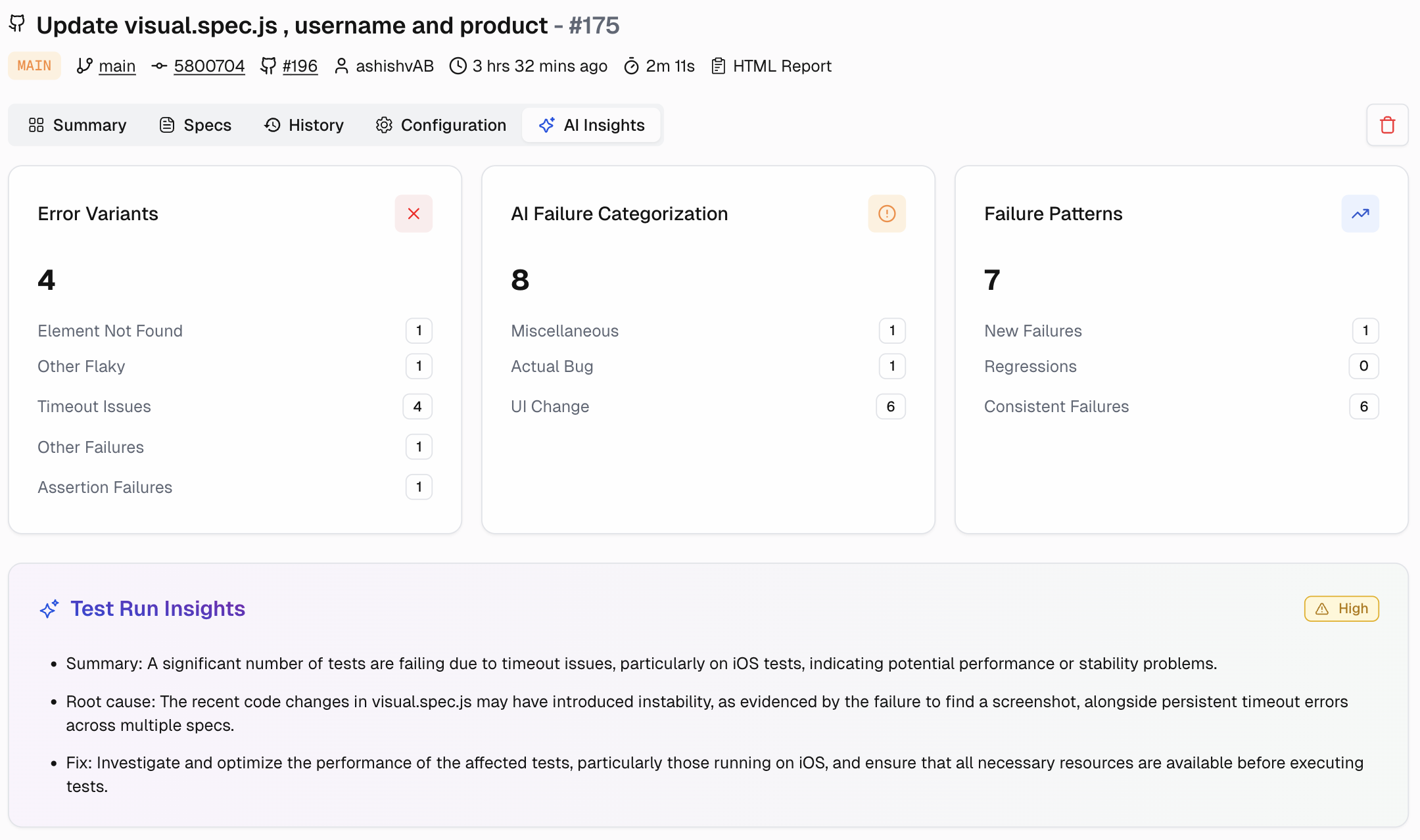
Test automation has a scaling problem. It’s not the test execution. It’s the maintenance.
One failing test. Then ten. Then you can't even tell if they're real failures or just noise. Your CI pipeline is effectively down. You're stuck debugging intermittent failures with no clear path to resolution. Now what?
Here's the thing: testing shouldn't be this painful. While your team wastes hours debugging false positives and waiting for 6-hour test suites, smart companies are running tests in 30 minutes with great accuracy. The difference?
They're using intelligent testing powered by AI and observability. This blog shows you exactly how to get there.