AI changes root cause analysis from a slow, manual process into a fast, automated one.
1. Real-time failure categorization and pattern detection
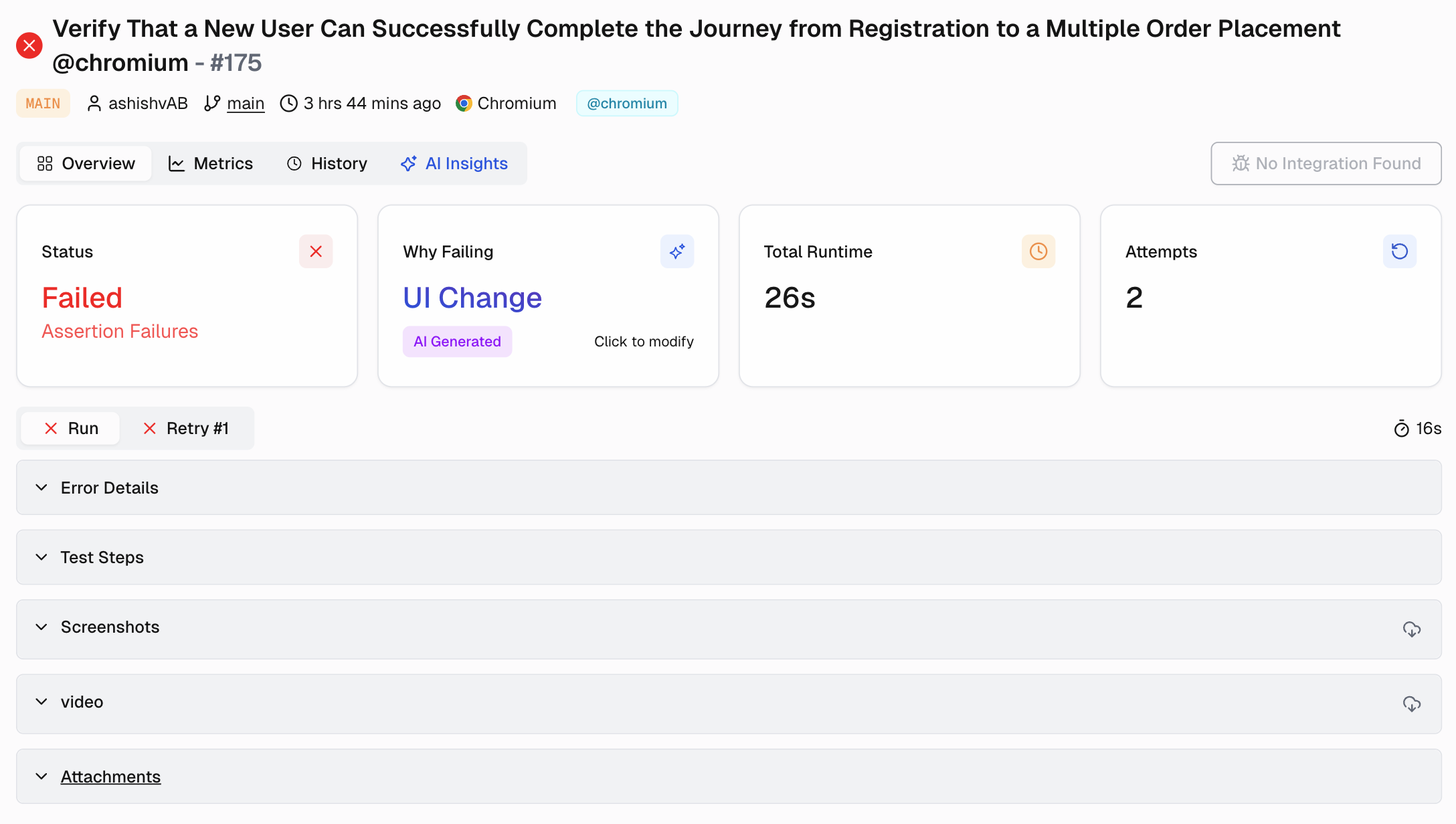
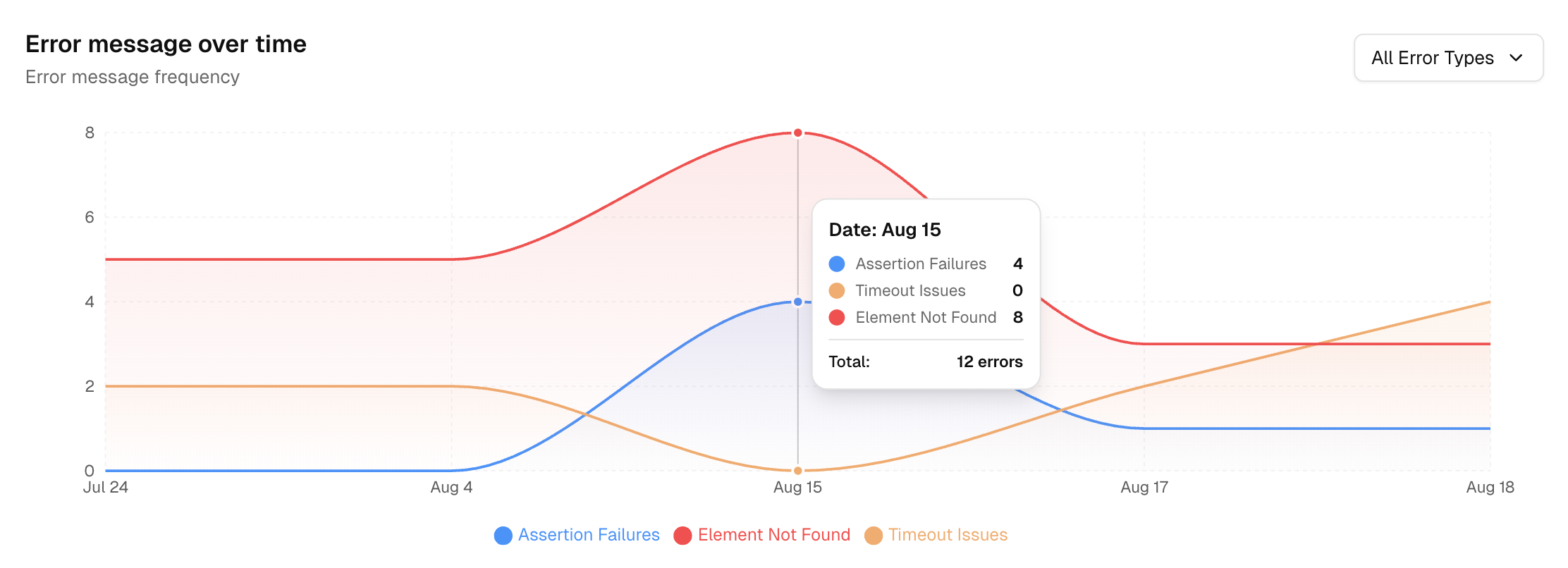
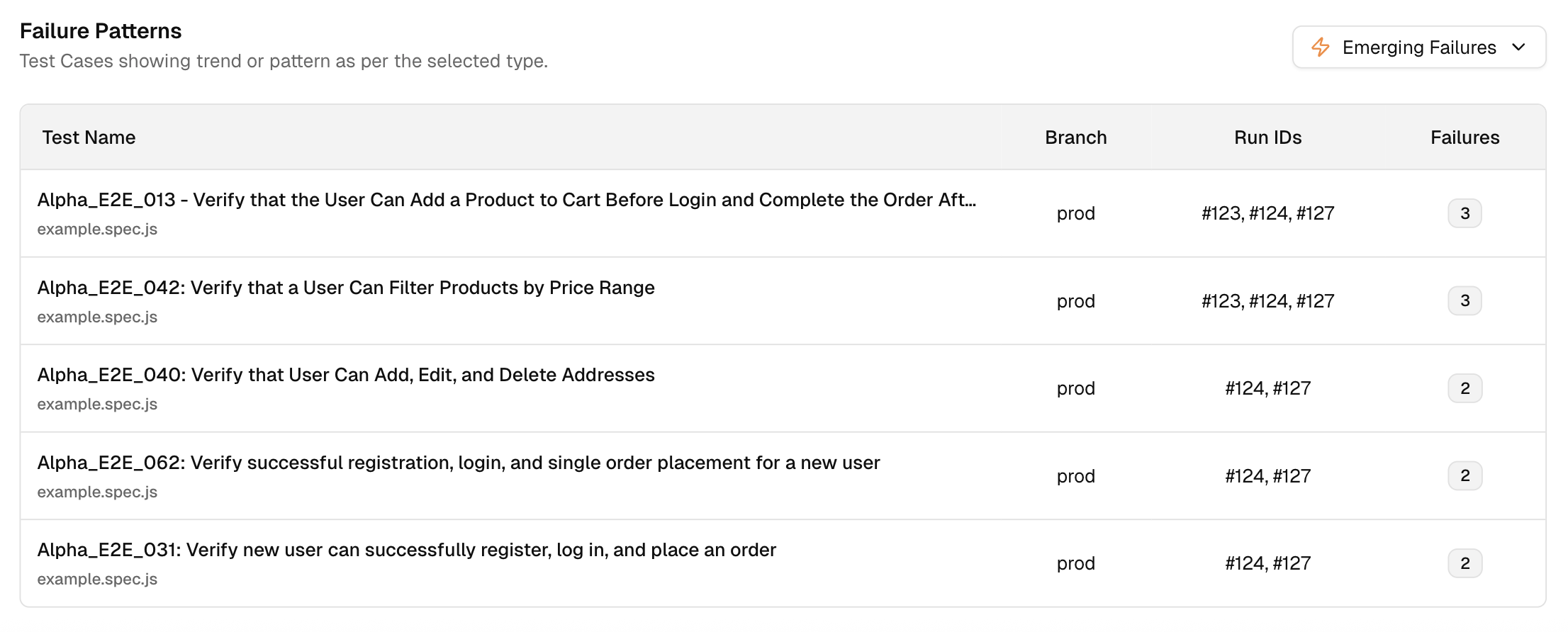
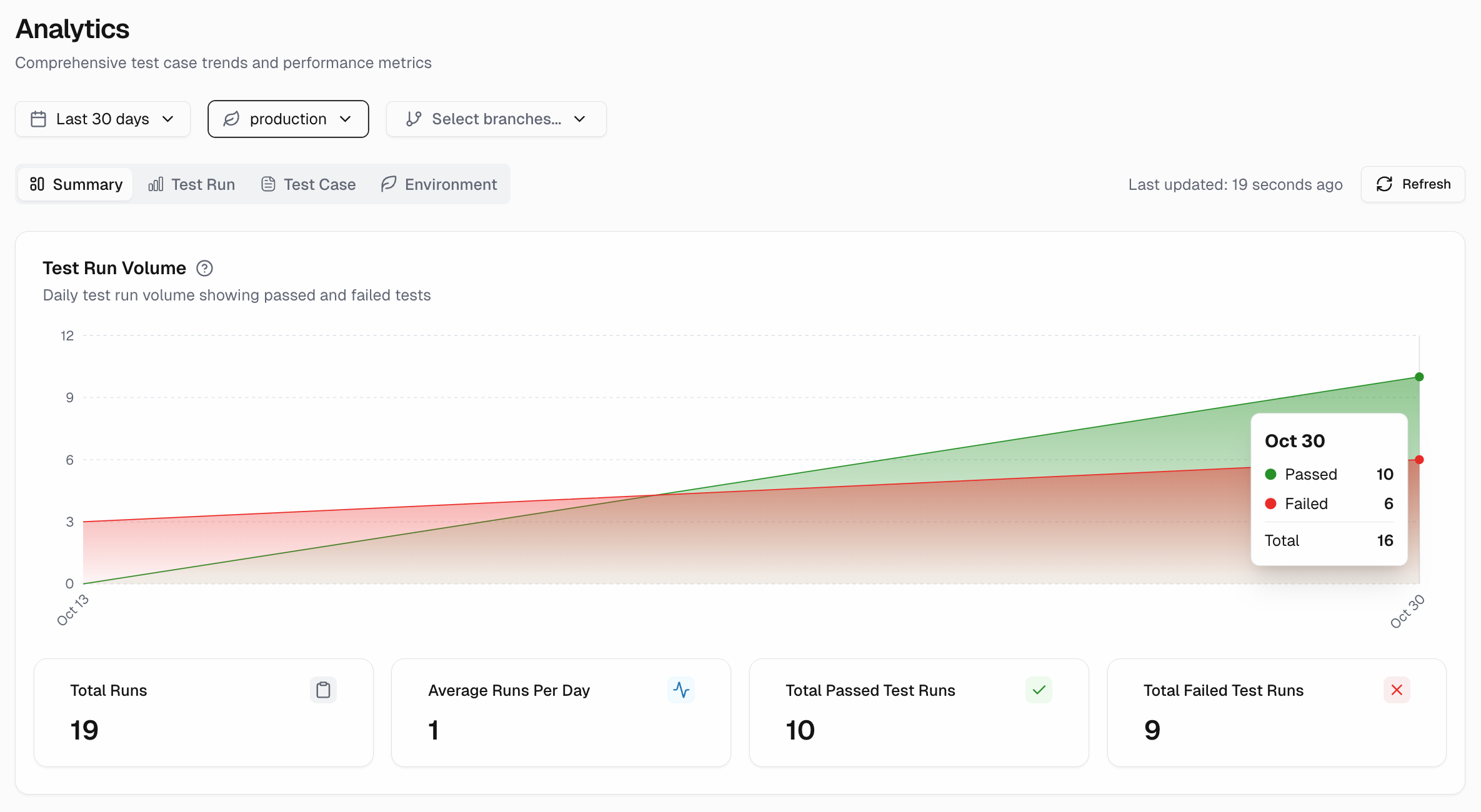
As soon as tests finish, AI algorithms analyze failures. They instantly classify them: “Product Bug,” “Environment Issue,” “UI Change,” “Flaky Test.” They group similar errors using pattern detection. This initial triage happens in seconds, separating critical signals from noise.
2. Automated correlation of logs, traces, and commits
This is AI’s superpower. It automatically connects the dots between logs, metrics, traces, and code changes that happened around the same time. AI leverages advanced analysis methods and RCA tools to automate the process, making root cause analysis faster and more reliable.
Modern tools utilize context IDs (such as trace IDs) to link all elements related to a single test execution. By integrating with Git, AI can often pinpoint the commit that caused the failure directly. This eliminates the hours spent manually correlating data.
3. Predictive insights for preventing future failures
AI doesn't just react; it learns. By analyzing historical failure data, code changes, and production incidents, machine learning models can predict future problems.
They might flag code areas prone to bugs or tests showing early signs of flakiness. This lets QA shift left, focusing tests proactively on high-risk areas.
4. Reducing false positives and test noise
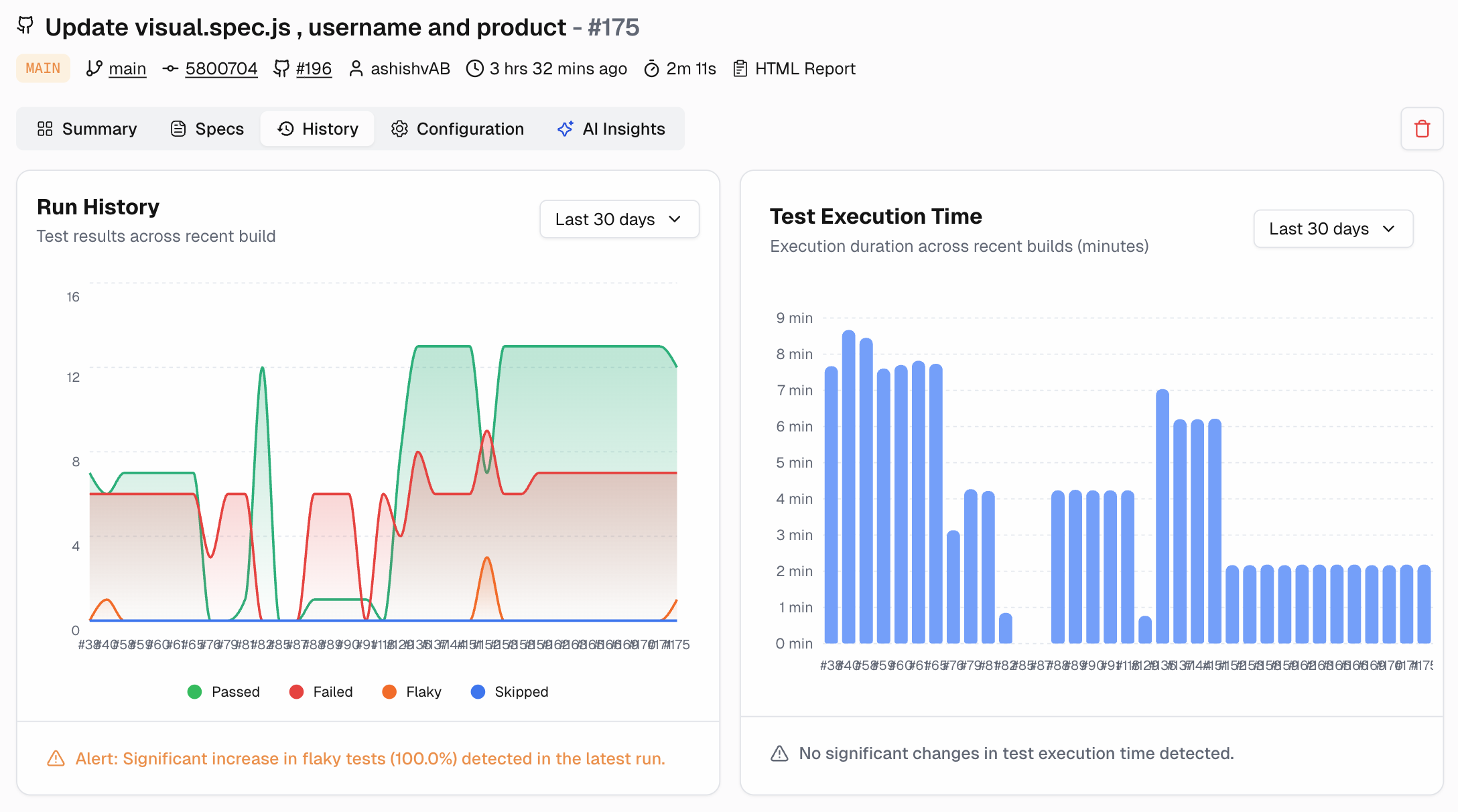
Flaky tests kill productivity. AI excels at spotting them. By analyzing pass/fail history, AI learns which tests are unreliable. It can flag them, suppress noisy alerts, or give them a low confidence score.
This ensures that developers are only paged for high-confidence failures that are likely real regressions.