Test automation in 2026 is no longer experimental or optional, especially as teams increasingly rely on Test Automation, modern Automation Tools, and intelligent Automation Frameworks to meet delivery demands.
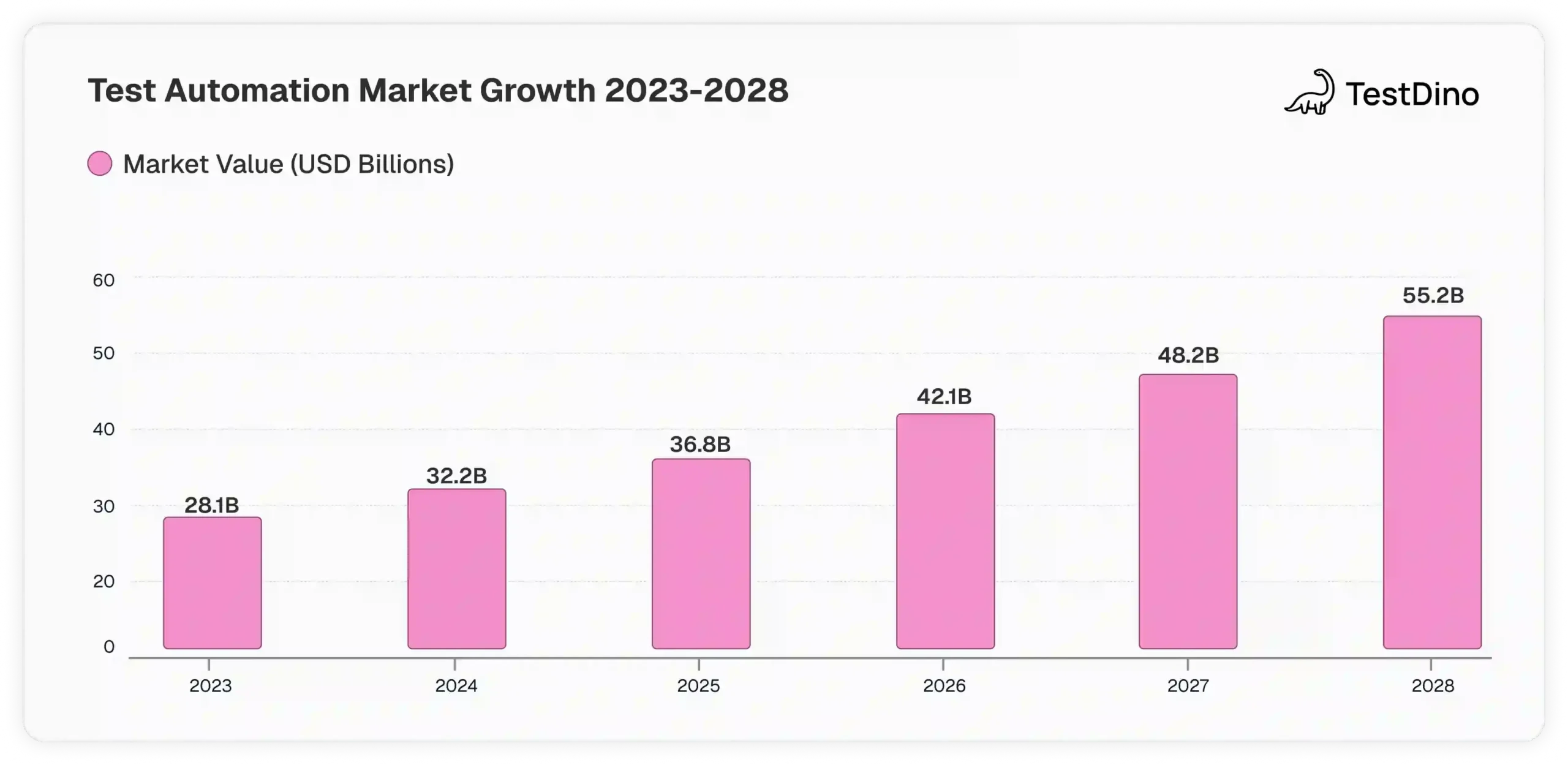
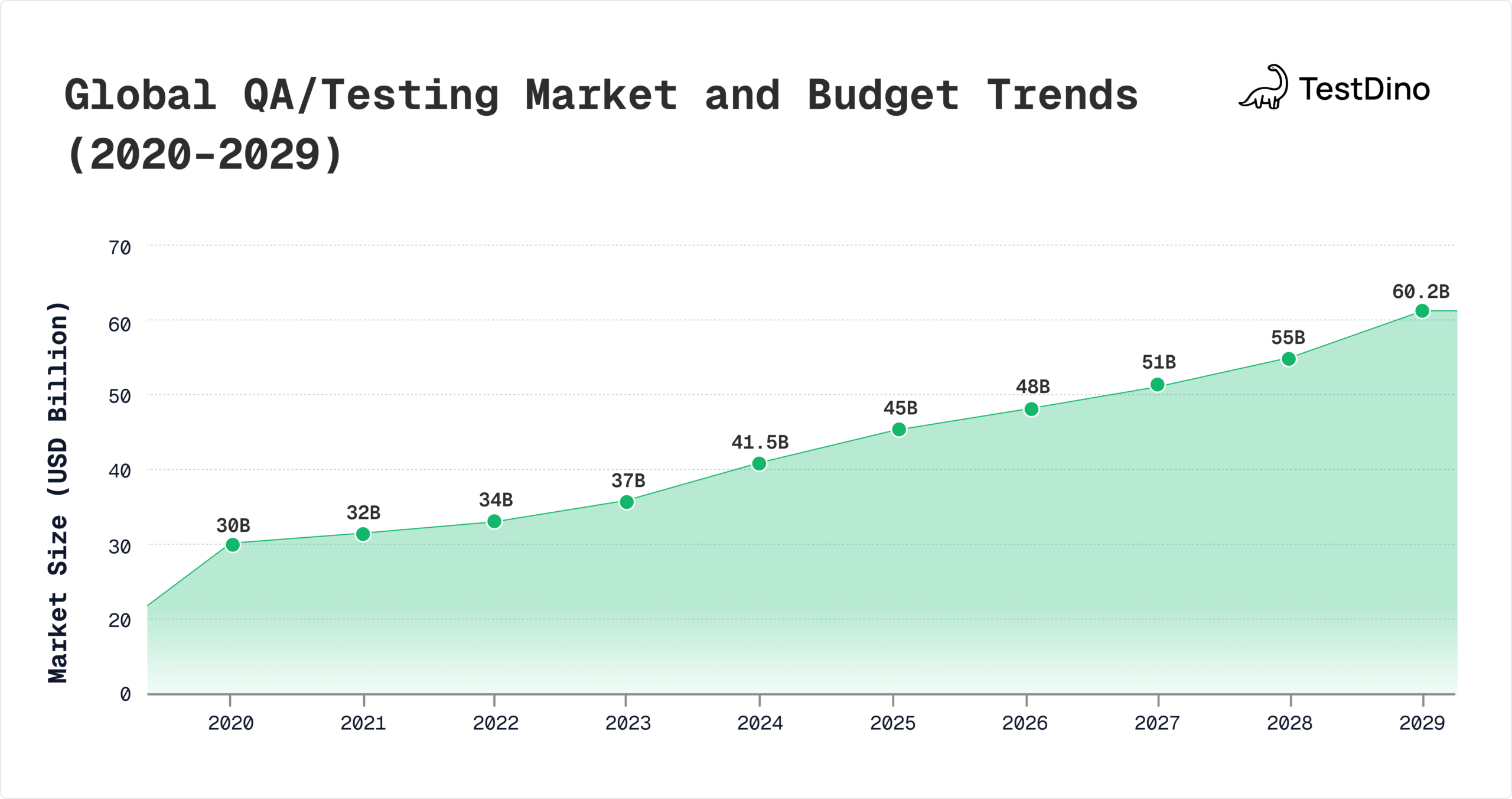
The global QA market now exceeds USD 41.5 billion and is projected to reach USD 60.2 billion by 2029, while the automation segment alone is set to nearly double from USD 28.1 billion in 2023 to USD 55.2 billion by 2028.
At the same time, adoption of AI-driven capabilities has surged, with 74% of enterprises using AI in testing according to McKinsey’s 2025 study, contributing to the rise of AI-Testing and smarter Self-healing capabilities embedded within frameworks.
This report compiles verified data from MarketsandMarkets, Gartner, McKinsey, and GitHub to highlight how automation frameworks, AI-assisted tooling, cloud execution, and DevOps integration are reshaping software quality worldwide.
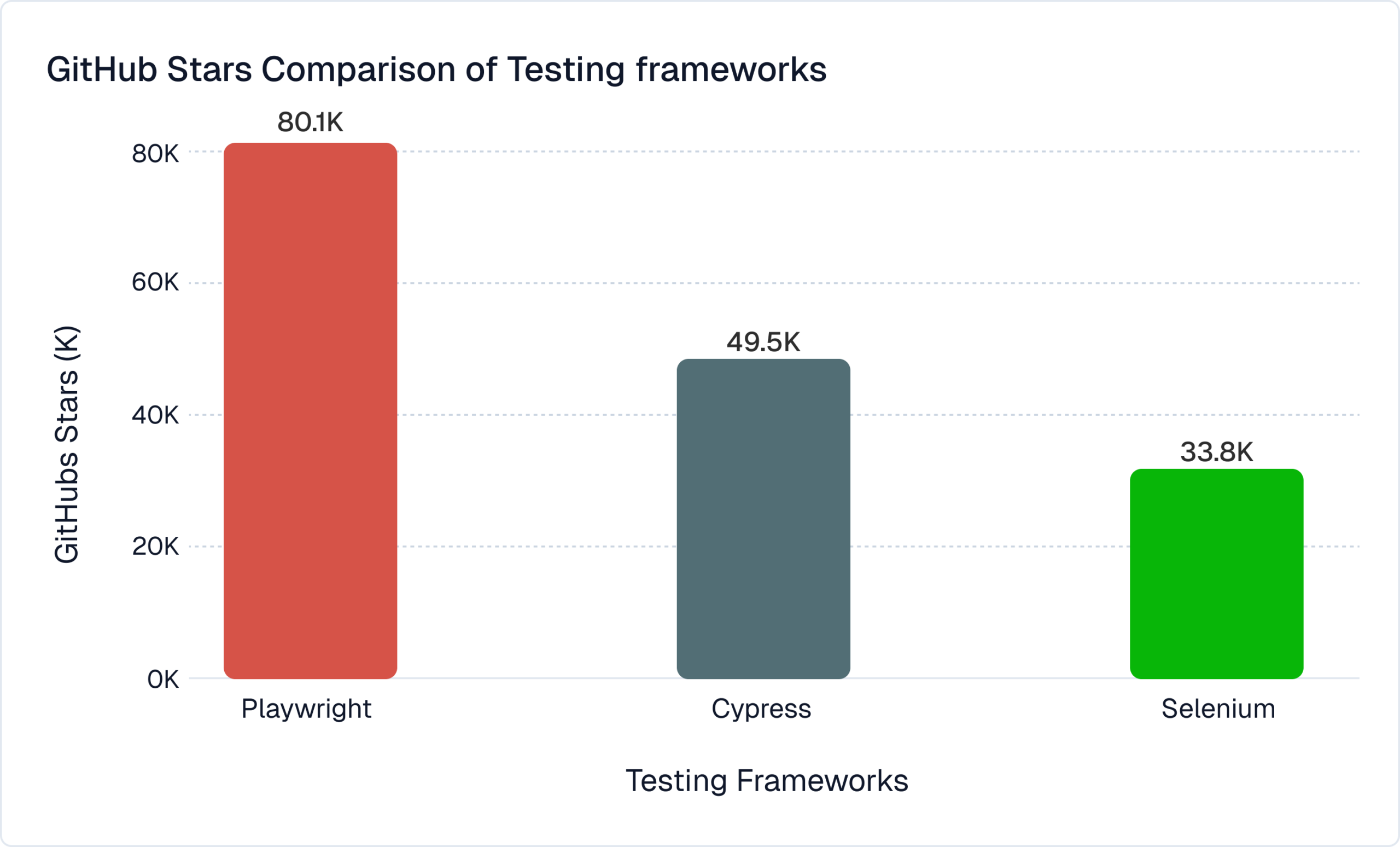
Whether you are selecting frameworks like Playwright, scaling automation coverage, or planning AI-based efficiency gains, the data here provides the context needed for clear strategy and informed decisions especially for teams using Continuous Integration and CI/CD pipelines.