Running automated tests is easy. Understanding them is not.
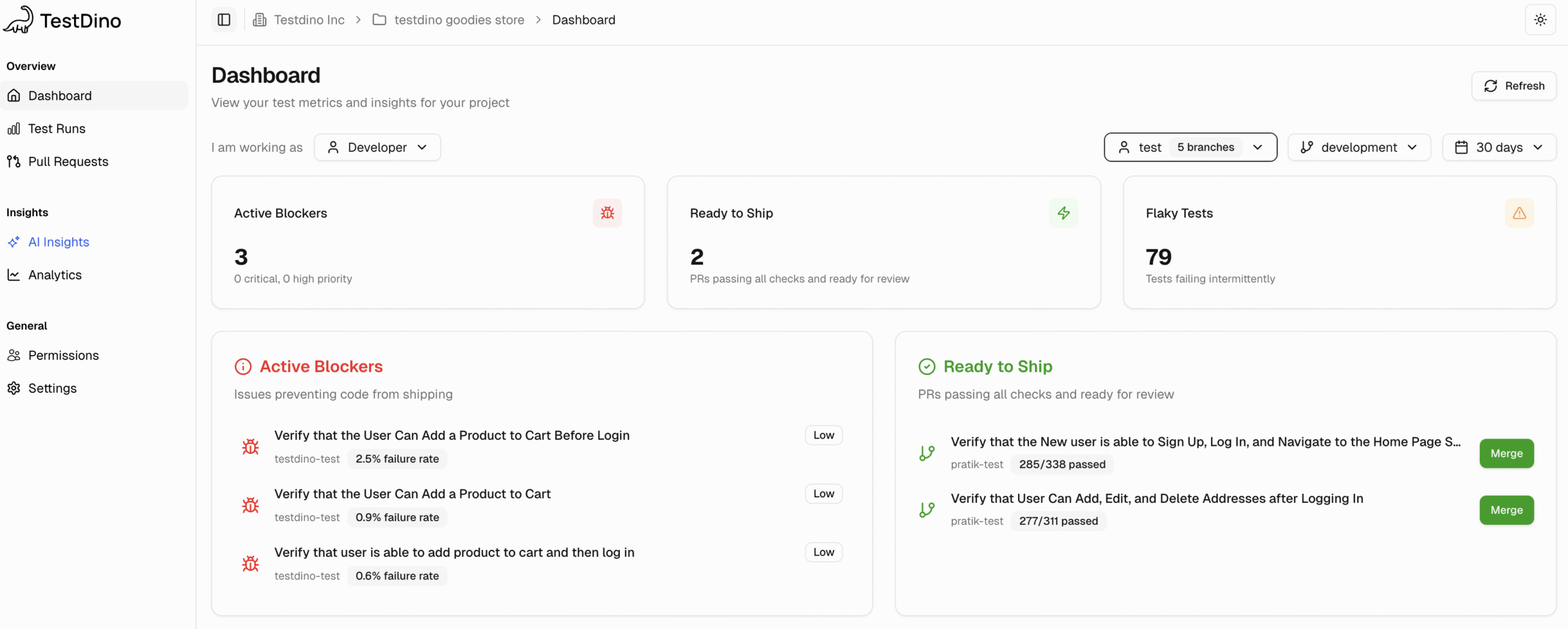
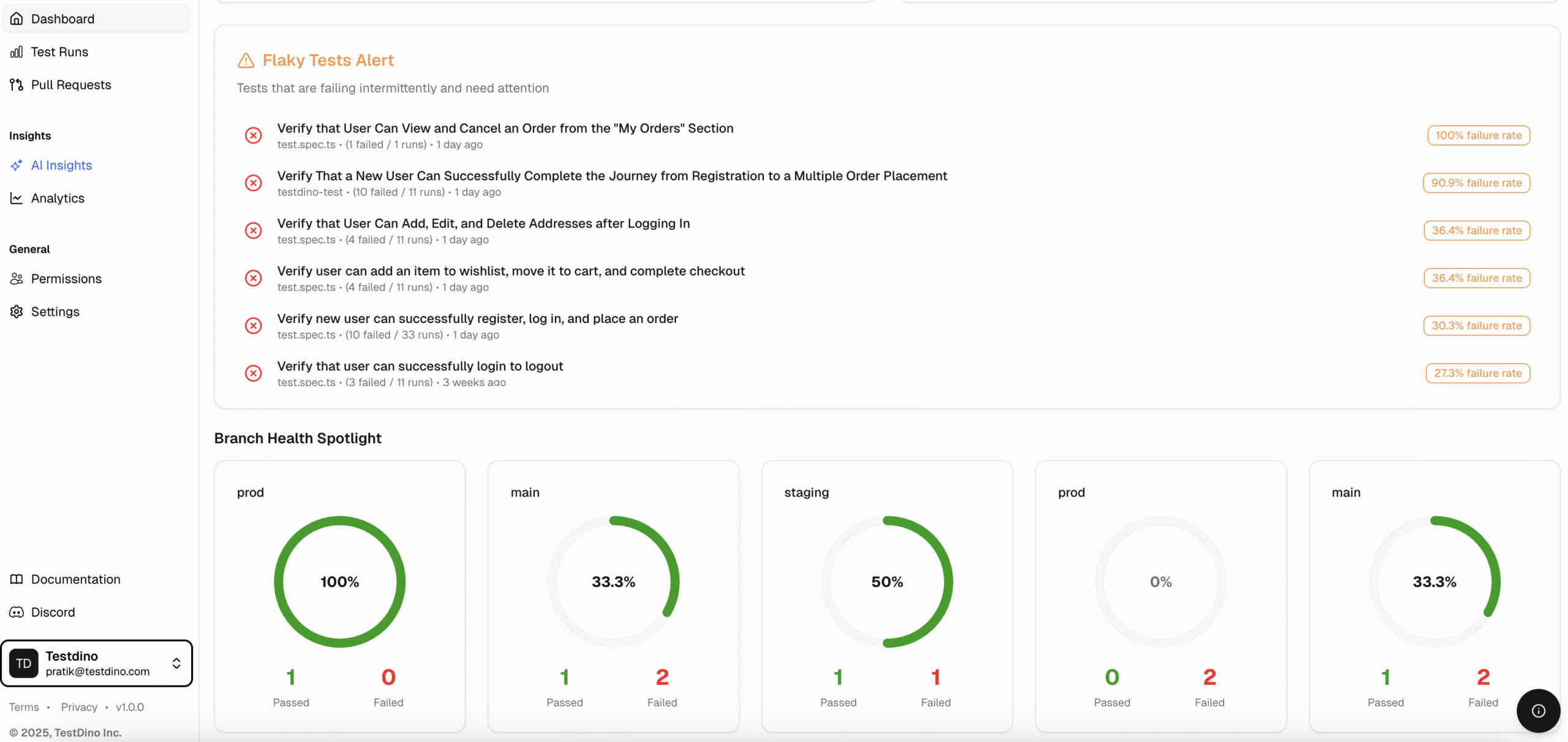
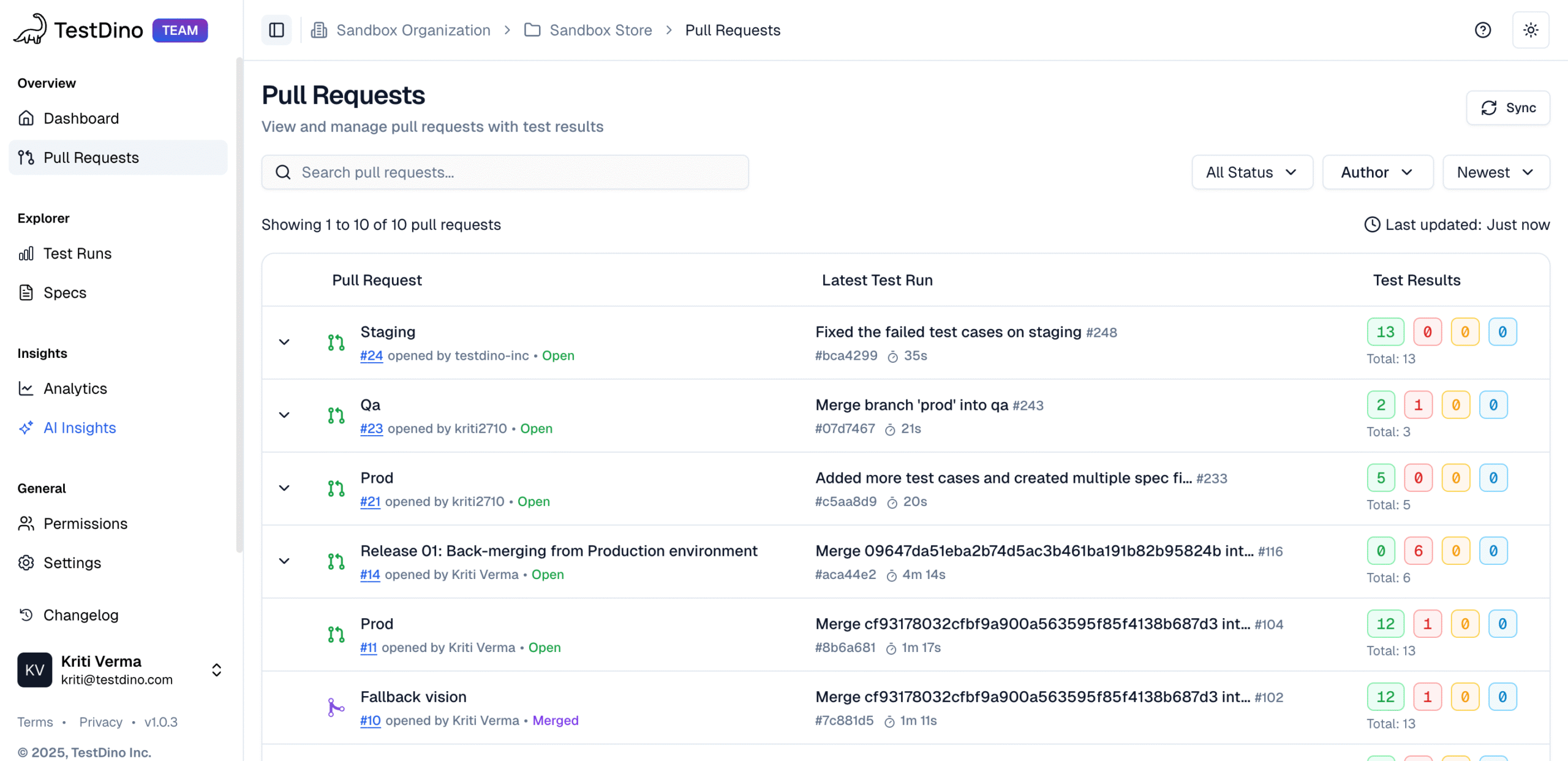
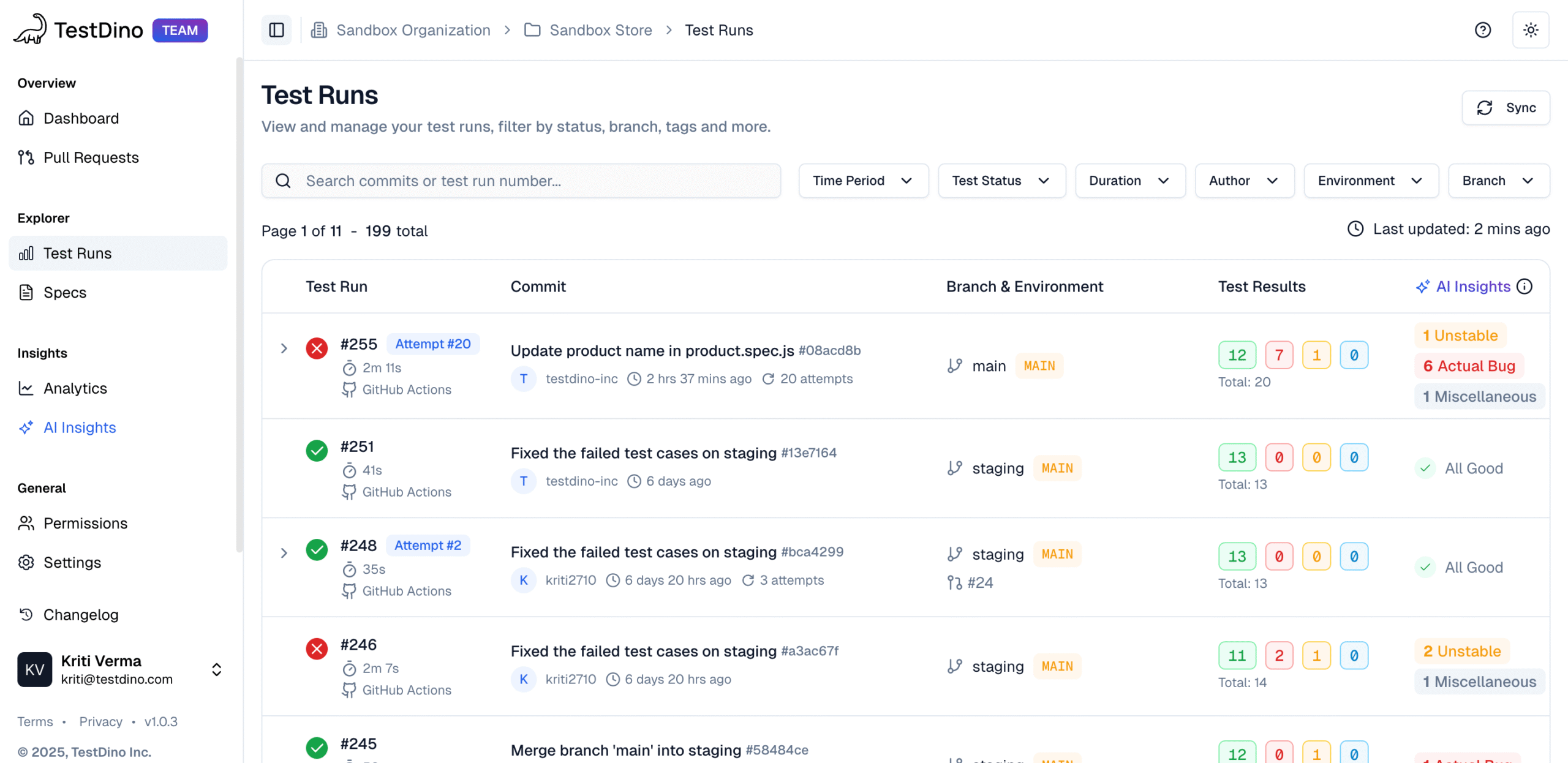
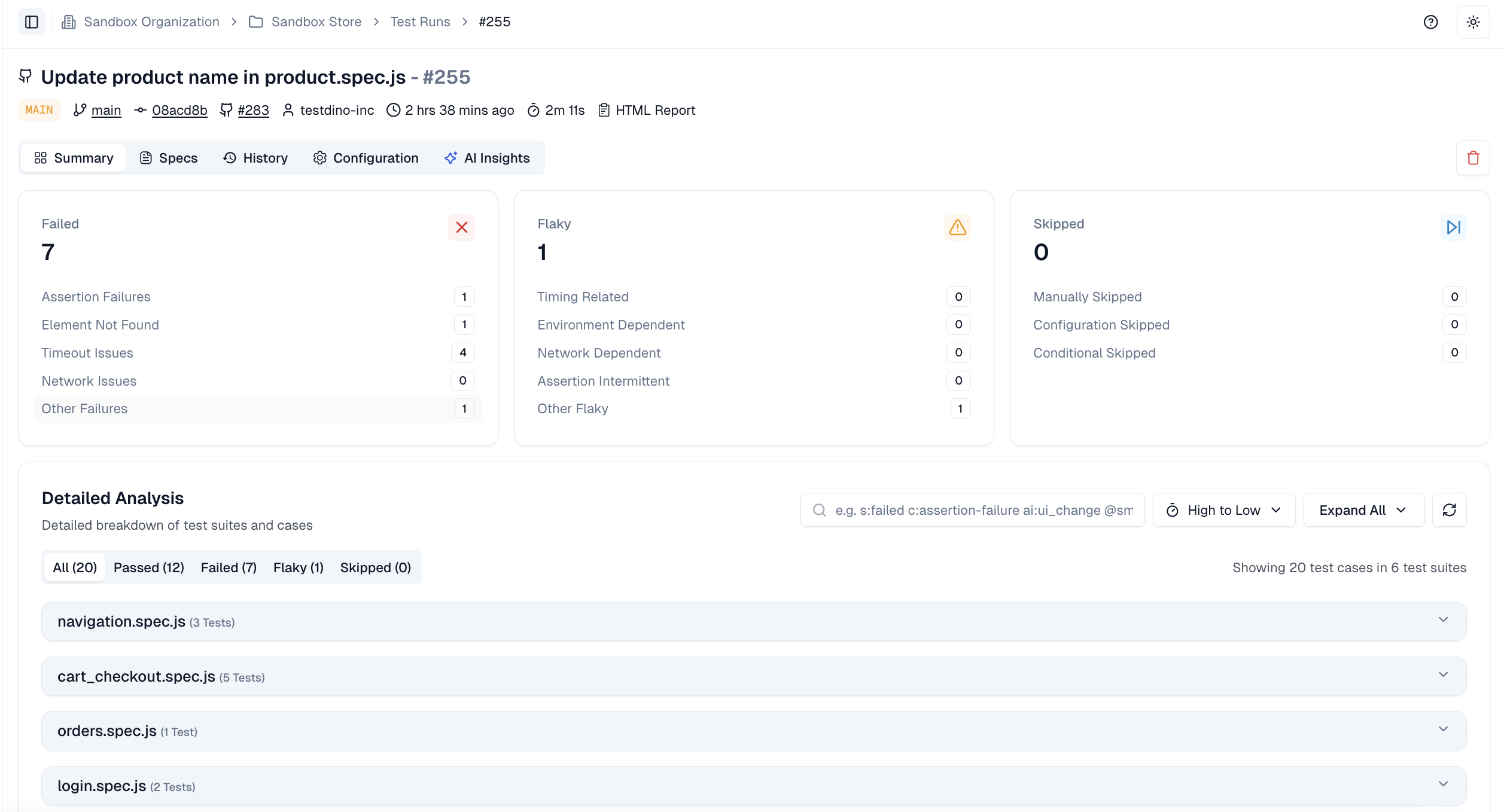
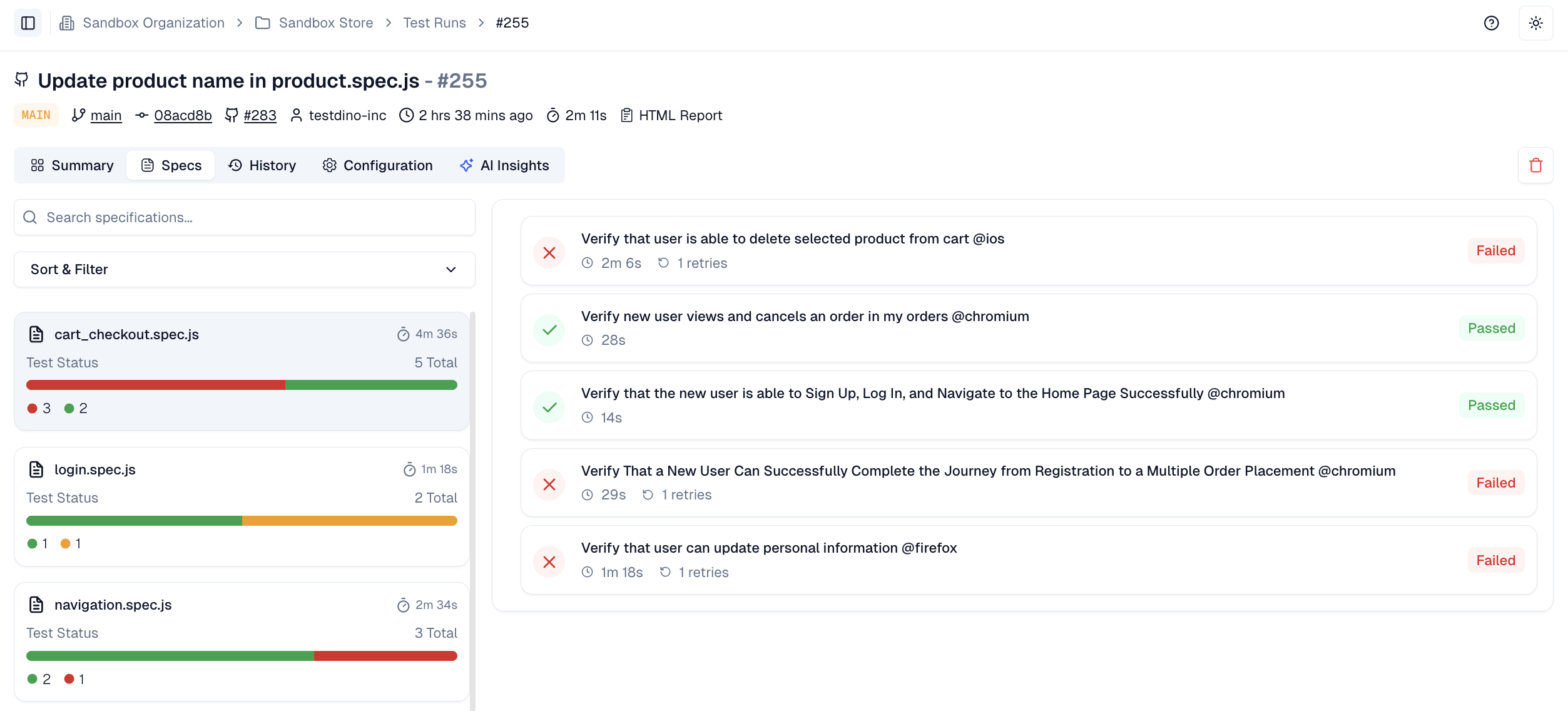
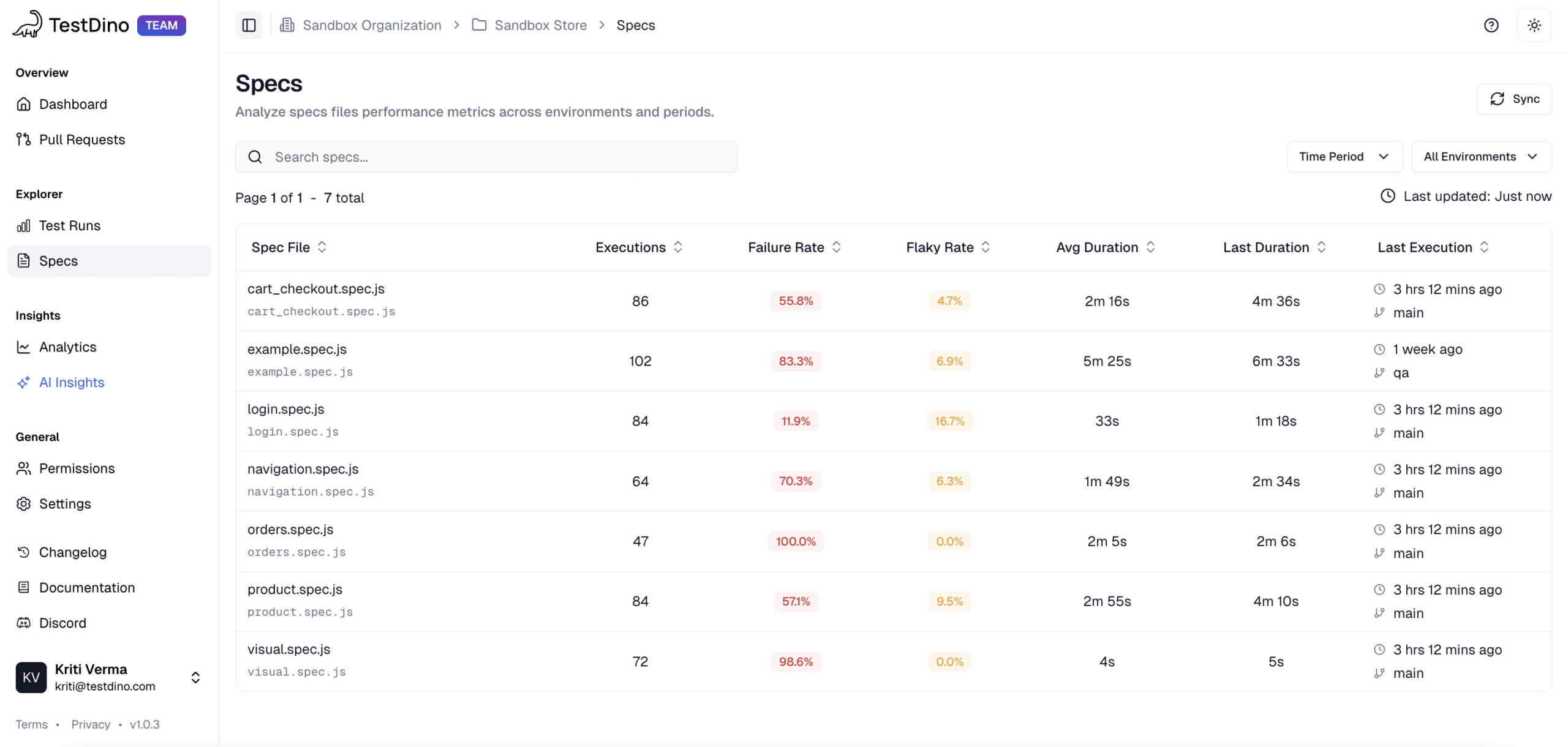
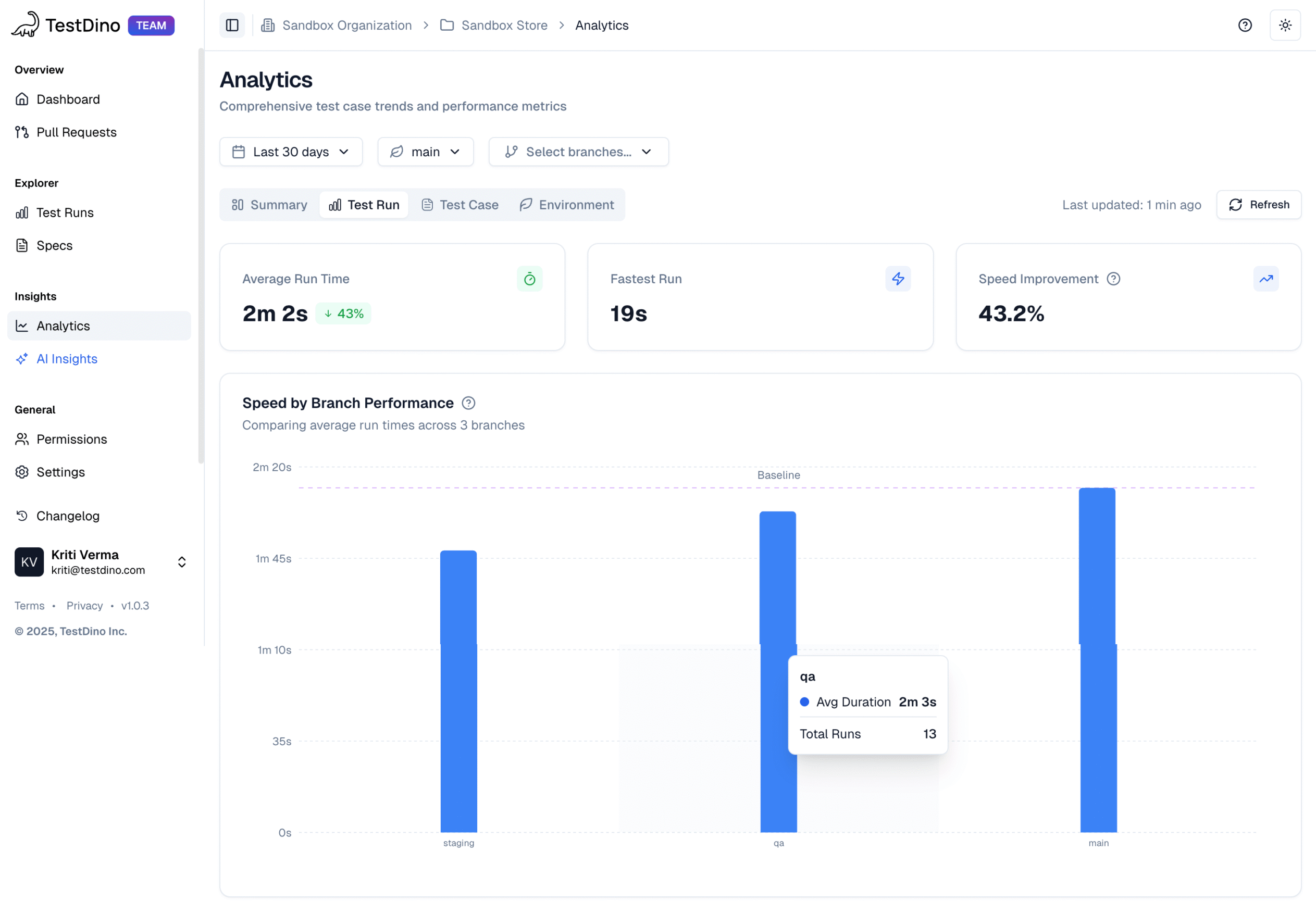
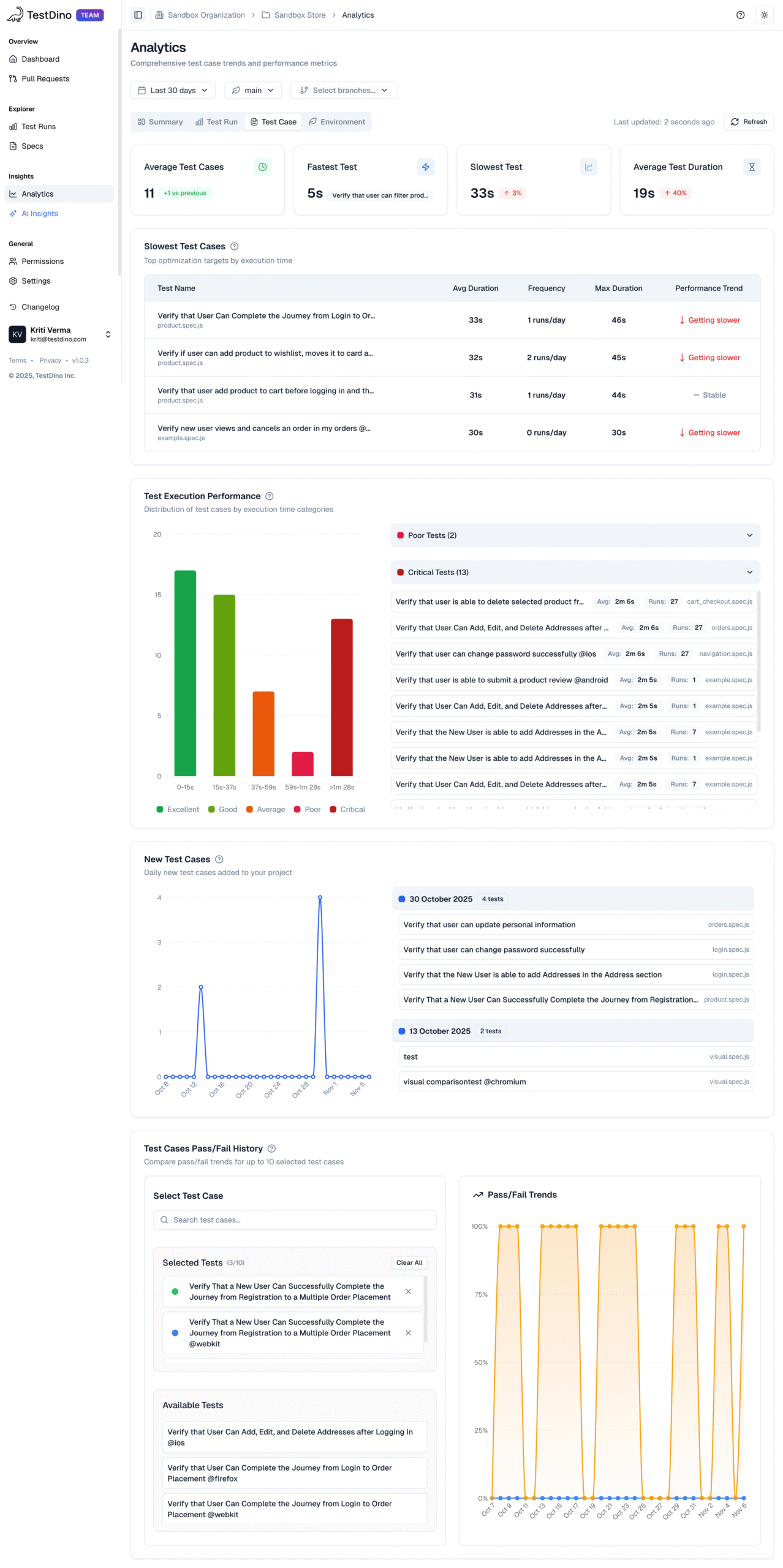
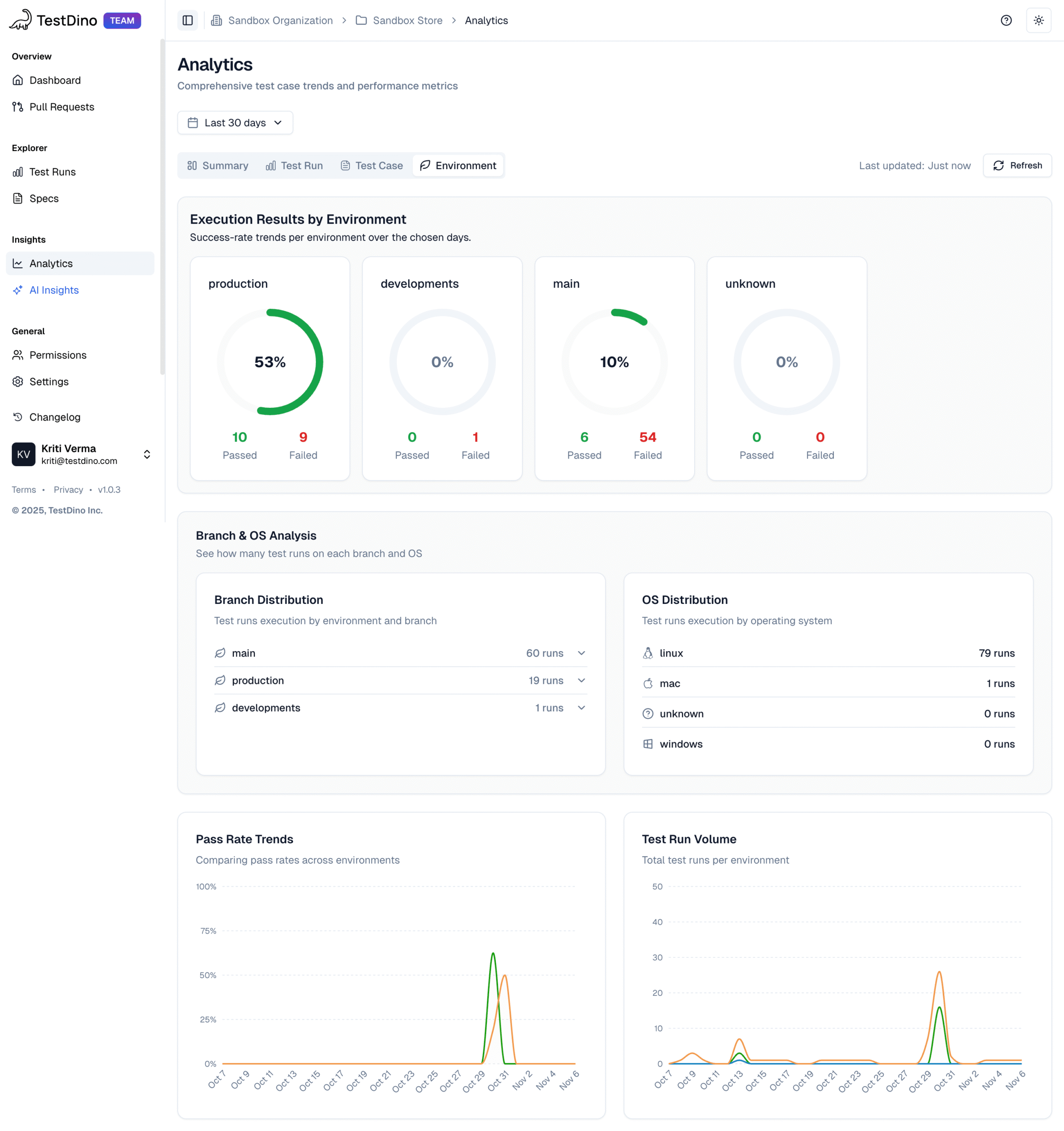
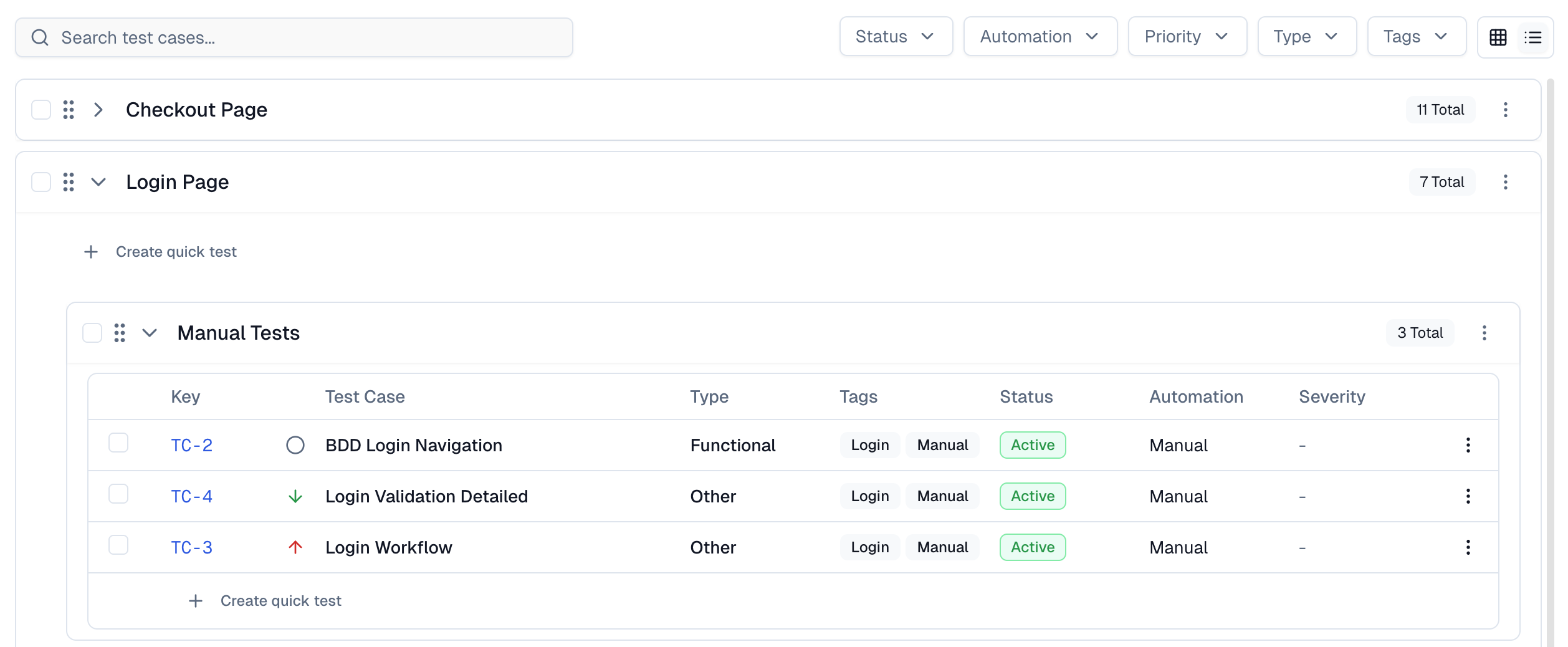
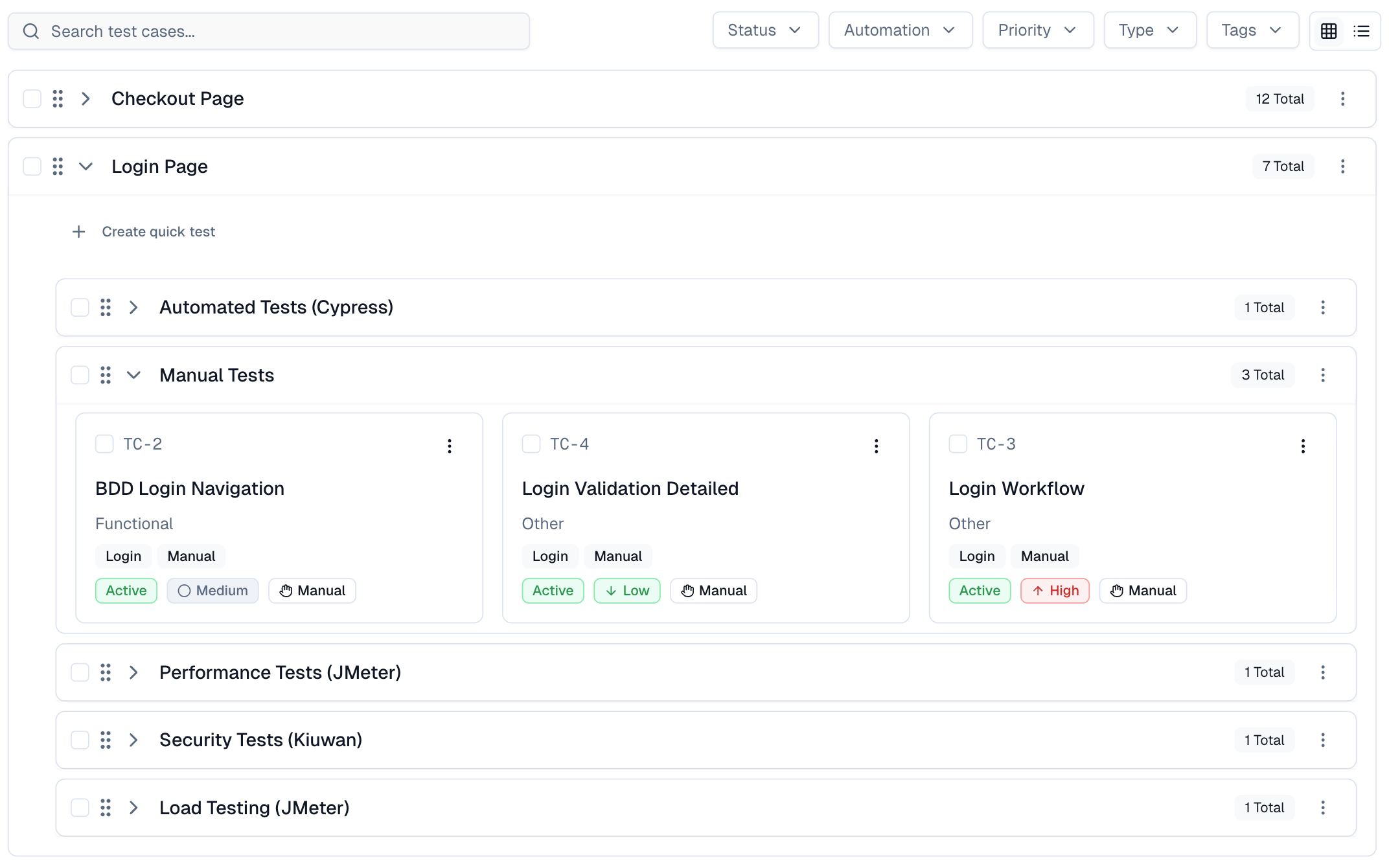
Most Playwright teams face the same daily struggle: thousands of test executions, endless CI logs, and countless pass/fail marks that reveal what happened but not why. Developers sift through CI pipelines, QA engineers fight flaky tests, and managers can’t see whether software quality is improving or slipping.
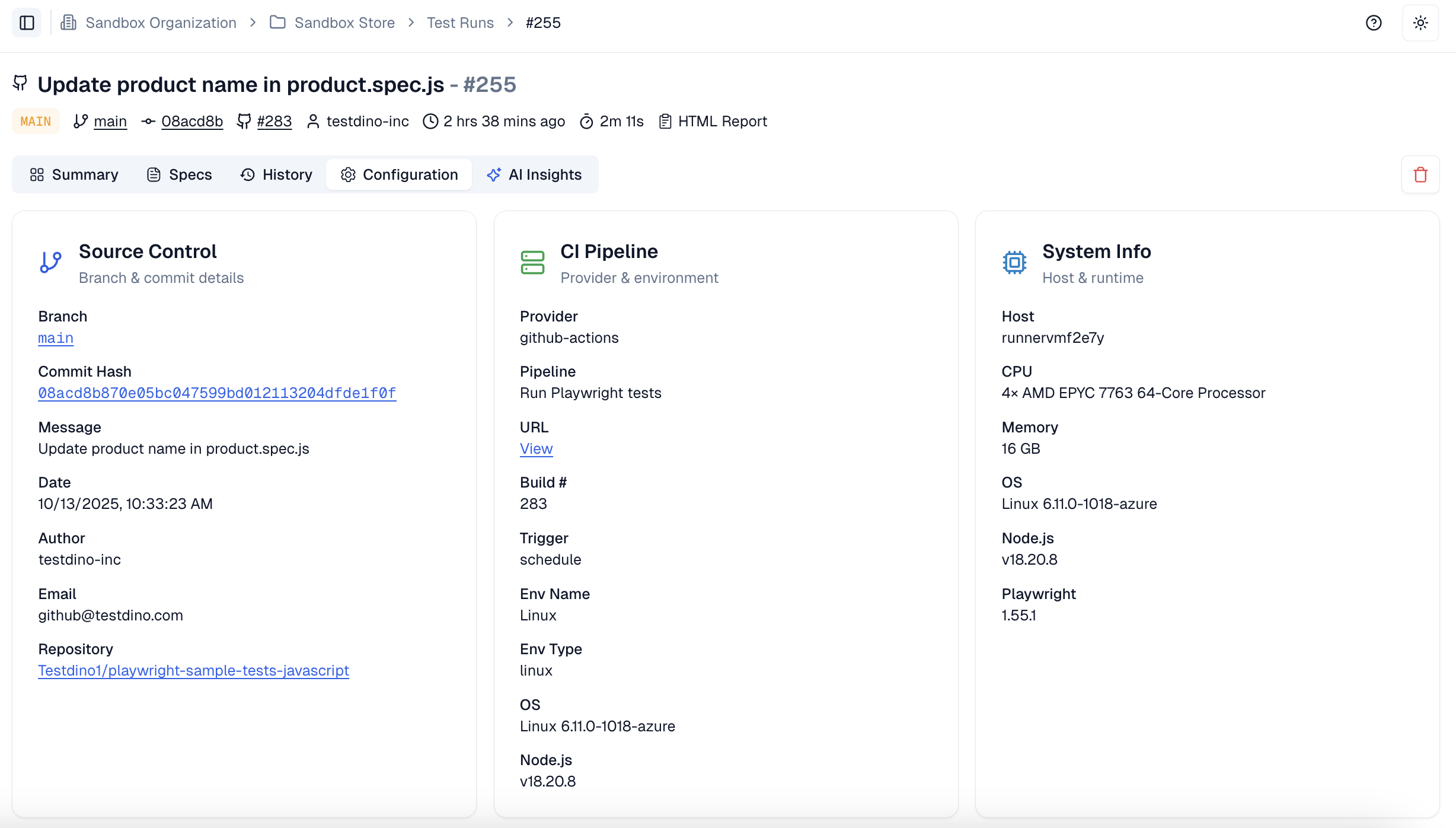
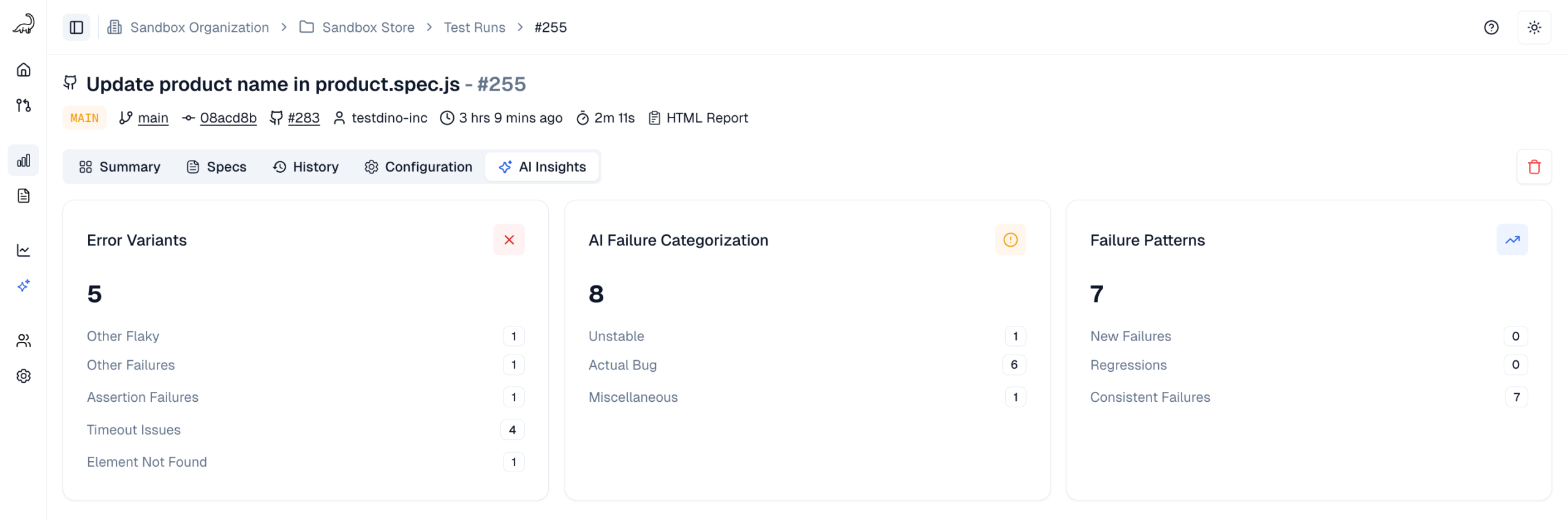
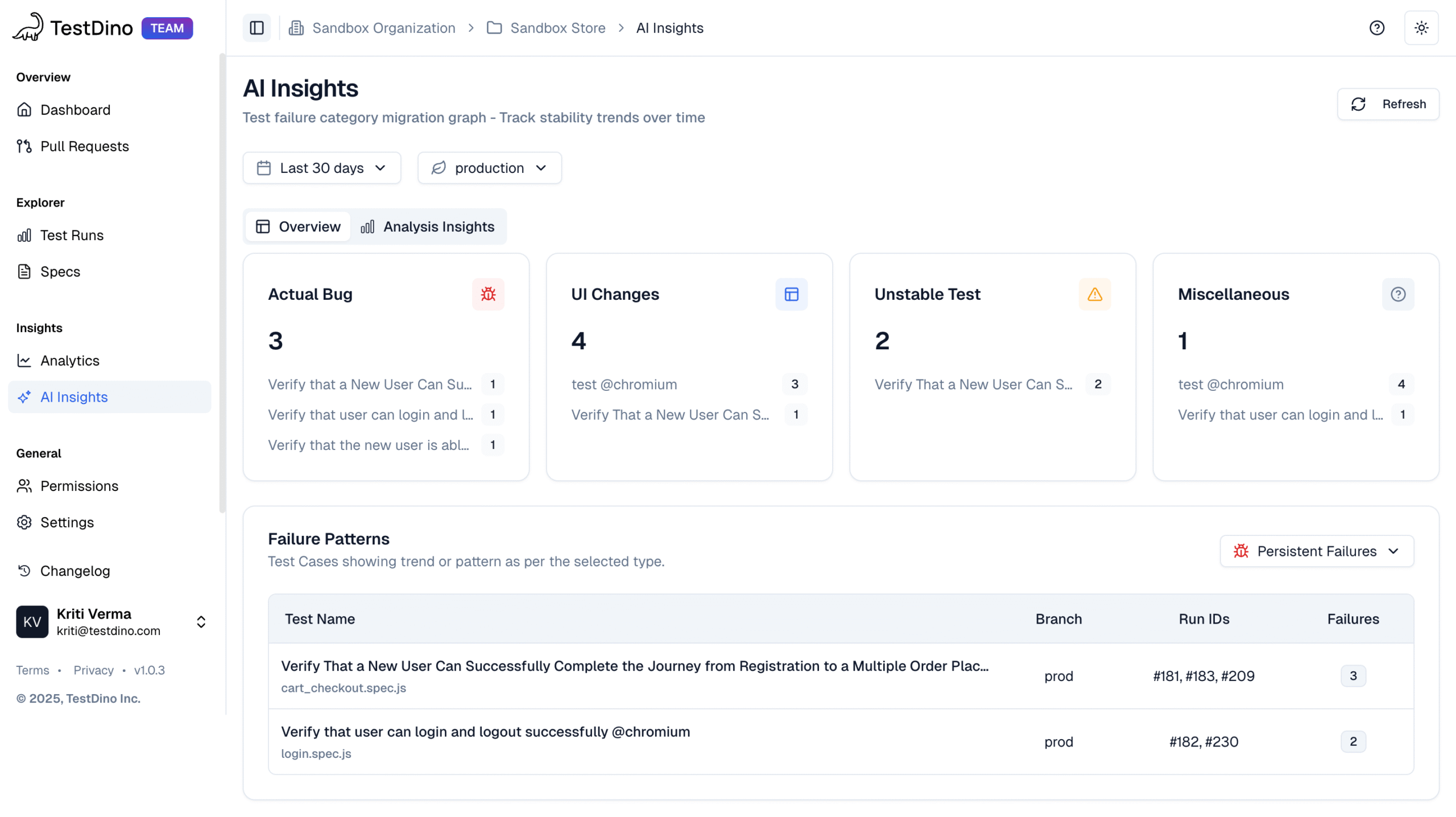
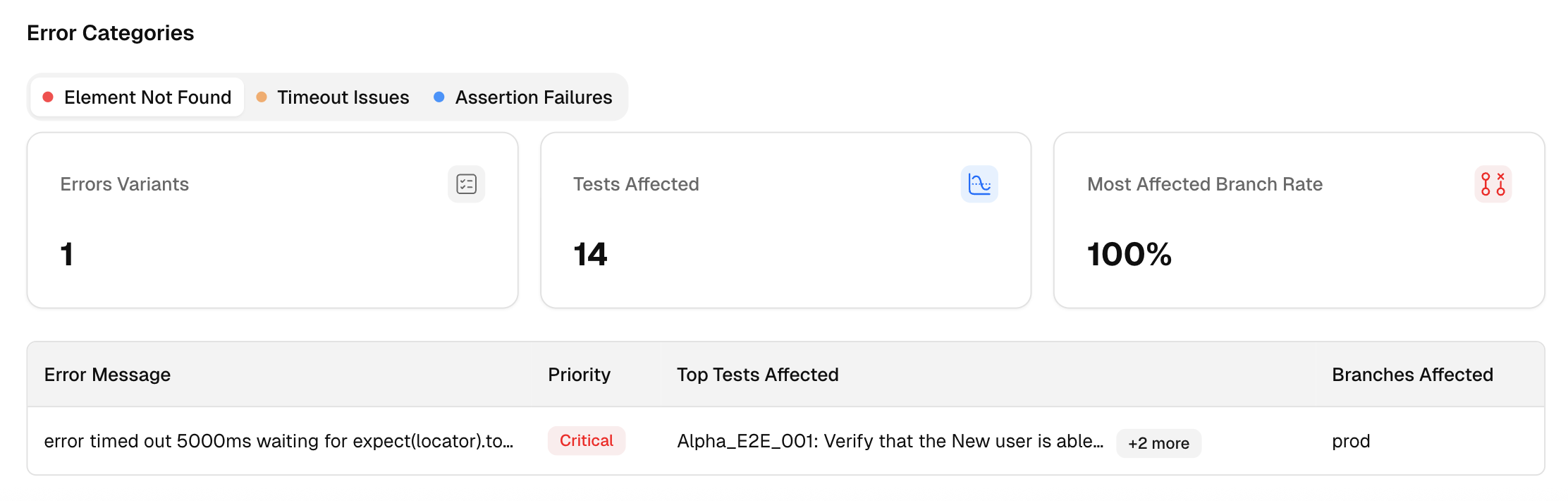
It goes beyond simple test reporting metrics, providing Playwright teams with a deep understanding of testing. Powered by AI failure categorization, role-based dashboards, PR-aware analytics, and detailed run evidence, it brings clarity to chaos.
It’s built for teams who care about clarity, not clutter, transforming Playwright test reporting into a source of actionable intelligence rather than noise.